With the help of information technology (IT), the operational, planning and control systems used in organizations are ongoing digitization and connections with each other.
Mobile and stationary systems of digitized companies communicate with each other horizontally and vertically via a common IT infrastructure in order to process and store data.
The main objective is always to realize the efficient implementation of business processes along the value chain and protect them appropriately against risks.
Especially the company’s critical assets and processes must be identified and evaluated in order to monitor their performance and defend them against unauthorized activities.
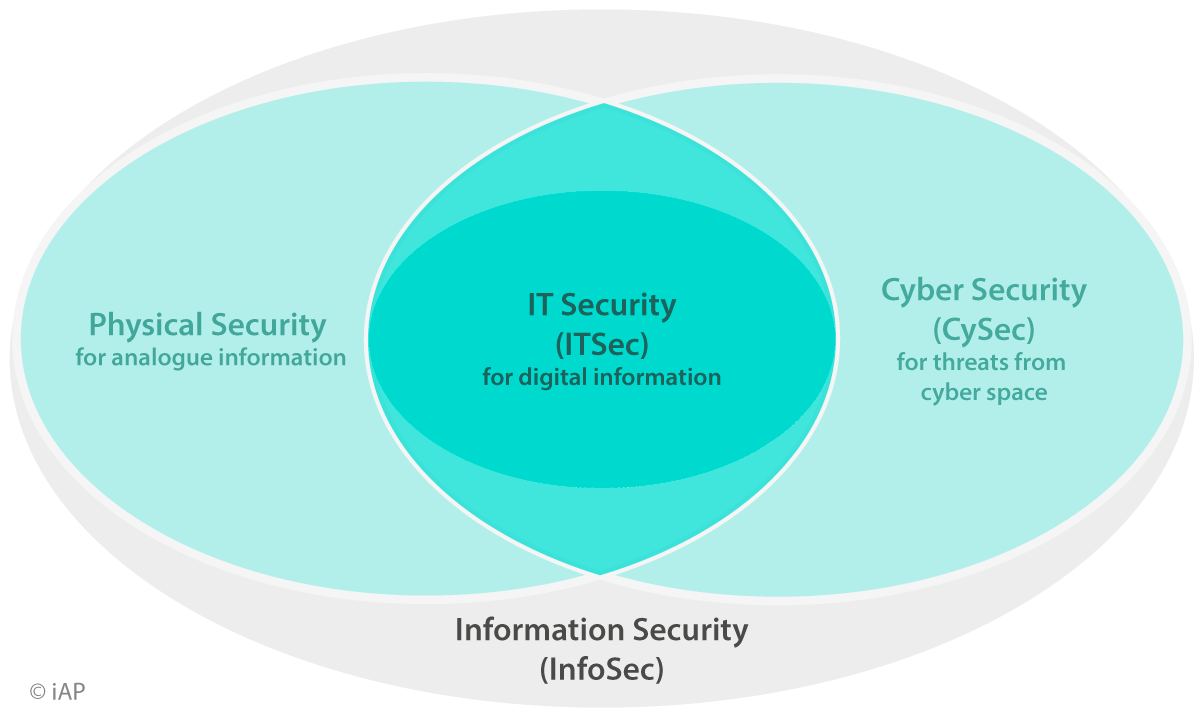
IT Security
IT Security (ITSec) aims to ensure correct performance and constant availability of all IT systems involved in providing business services and to guarantee integrity as well as confidentiality of digital company data.
Cyber Security
Cyber Security (CySec) extends the protective measures of IT-Security to the cyber space surrounding an organization. Due to the necessary communication and data transfer via the Internet, the attack surface of every company increases. Cyber-Security focuses on necessary methods and tools based on a dedicated analysis of the cyber threat landscape. This includes various types of threats such as Malware, Ransomware, Botnets, DDos as well as Man-in-the-Middle attacks and Social Engineering with Phishing attacks. In addition, possible attacker types are considered in order to avoid their attack and spying attempts.
Information Security
Information Security (InfoSec) considers all digital as well as analogue data and includes all technical and non-technical protective measures to ensure the organization’s information protection goals of availability, confidentiality, integrity and authenticity (VIVA). Technical and organizational measures (TOM) are implemented by Information Security Management (ISM) with the help of IT- and Cyber-Security.
Cyber Security Risks
Risks are calculated from the probability of damage and the determination of the amount of damage for a possible cyber attack. Simply considering the risks of cyber attacks is not enough. It is important to start further down or up.
During the processes of digitization, almost every organization is struggling with the challenges of defining or designing its strategic security goals and functional processes in order to avoid unwanted cyber security incidents.
There is insufficient awareness among the responsible employees of
- relevant compliance and governance requirements
- appropriate analyses of company’s processes and related IT assets
- comprehensive process and risk-related collection and evaluation of company threat data, e.g. possible attackers with attack types and targets
- actual company needs to adapt organizational and technical security measures and to create an appropriate level of protection
- the baseline due to insufficient understanding of the actual and target states
- the need for budget as well as capable and experienced staff at all levels
- the efficient selection, integration and application of appropriate security tools
- Security Standards e.g. ISO27XXX and 22301, BSI 200-X & C5, NIST, BAFIN, CSA, NIST 2








 ustainability & ESG
ustainability & ESG
